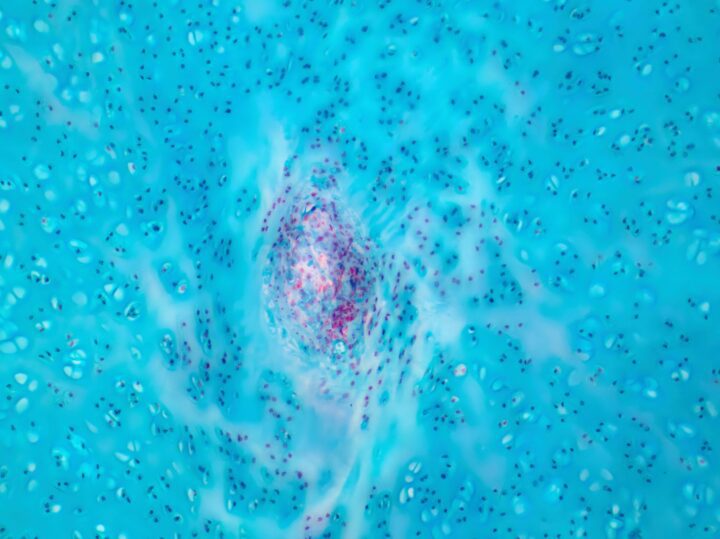
TISSIUM are proprietary polymers that enable tissue reconstruction and adhesion.
Benefits
- Multi-use
- Biocompatible
Applications
- Medical adhesives
- Tissue engineering
- 3D printed implants
- Drug delivery
UN Sustainable Development Goals Addressed
-
Goal 3: Good Health & Wellbeing
The Challenge
Tissue reconstruction after surgery presents many challenges. The tissue must be fully restored to its natural function while keeping scarring to a minimum. Traditional medical adhesives, such as glues or staples, are often not biodegradable and can sometimes cause further damage to the tissue.
Innovation Details
TISSIUM™ is a group of proprietary s inspired by fibrous keratins found in skin. The polymers can conform to and integrate with surrounding tissue in order to enable tissue reconstruction. It works by activating a viscous pre-polymer with a visible blue light. The resulting bond is both adhesive and elastic, allowing the polymer to comply with the underlying tissue while remaining strongly adhered. The polymer building blocks enable customization to match the tissue-specific requirements of specific therapeutic areas. The polymers could be integrated with peripheral nerve, gastrointestinal and cardiovascular systems. The pre-polymer can also be used as a resin to build high-resolution 3D-printed devices, or pre-loaded with drugs to use as a delivery system at multiple locations within the body.
Biological Model
Skin needs to protect the body while still being able to exchange water and ions. Fibrous keratins help to strengthen skin while simultaneously providing a structural support for lipids, which control the flow of liquids, primarily water, across the skin.