Navigate Through Liquid
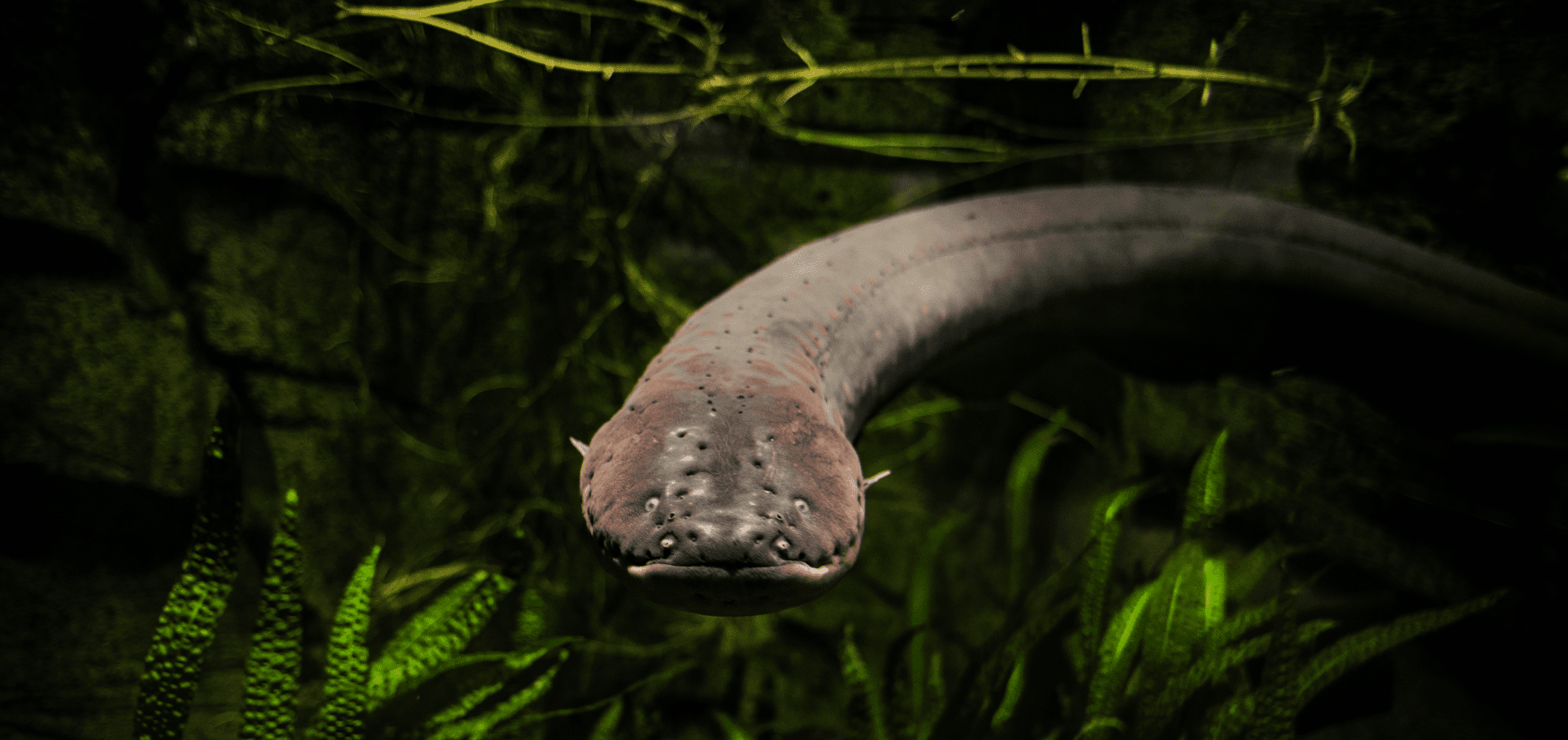
Living systems that move in liquids must navigate around physical obstacles and find their way from place to place to locate resources or suitable climates. Many liquids are denser than air, which means it’s a thicker medium through which signals must pass. On the other hand, liquids tend to conduct some signals better than air or solids. Liquid dwellers must use strategies that enable them to detect and follow signals in this dense medium. For example, electricity transmits well in water and several organisms, such as Amazon electric eels, have organs that detect and use electric signals to navigate.
Modify Electric Charge
Harnessing the power of electricity can be a powerful way for organisms to get energy. An electric charge can be positive or negative. When matter with an electric charge is near other charged particles, it will either be ‘repulsed’ or ‘attracted’ to the matter based on the charge. From electric eels to oriental hornets, learn about the different ways organisms use electric charges to their advantage.
Capture, Absorb, or Filter Organisms
Many living systems must secure organisms for food. But just as one living system must capture its prey to survive, its prey must escape to survive. This results in capture and avoidance strategies that include trickery, speed, poisons, constructed traps, and more. For example, a carnivorous plant called the pitcher plant has leaves formed into a tube that collect water. Long, slippery hairs within the tube face downward. When insects enter the tube seeking nectar, they lose their footing and slide inside, unable to climb out and escape being eaten and digested by the plant.