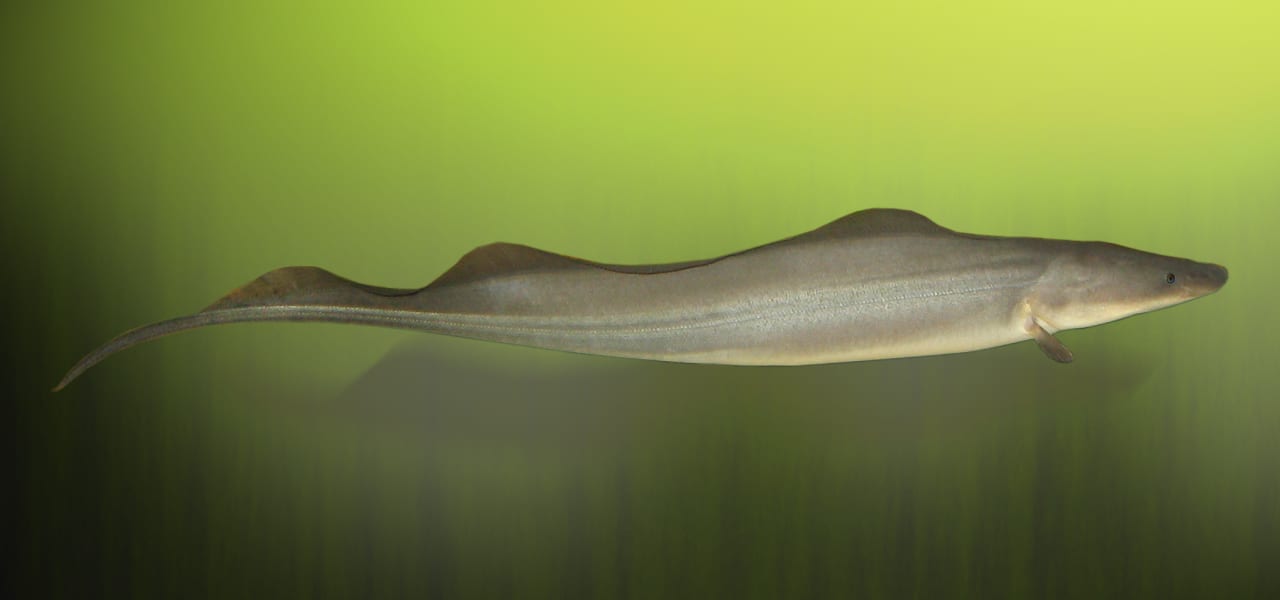
Undulations of the tail and dorsal fins of the African freshwater electric eel allow for smooth bidirectional movement through the water.
“In addition to forward undulatory swimming, Gymnarchus niloticus can swim via undulations of the dorsal fin while the body axis remains straight; furthermore, it swims forward and backward in a similar way, which indicates that the undulation of the dorsal fin can simultaneously provide bidirectional propulsive and maneuvering forces with the help of the tail fin.” (Li et al. 2005:115)