Move in/on Liquids
Water is not only the most abundant liquid on earth, but it’s vital to life–so it’s no surprise that the majority of life has evolved to thrive on and under its surface. Moving efficiently in and on this dense and dynamic substance presents unique challenges and opportunities for living systems. As a result, they have evolved countless solutions to optimize drag, utilize surface tension, fine tune buoyancy, and take advantage of various types of currents and fluid dynamics. For example, sharks can slide through water by reducing drag due to their streamlined shape and specially shaped features on their skin.
Modify Buoyancy
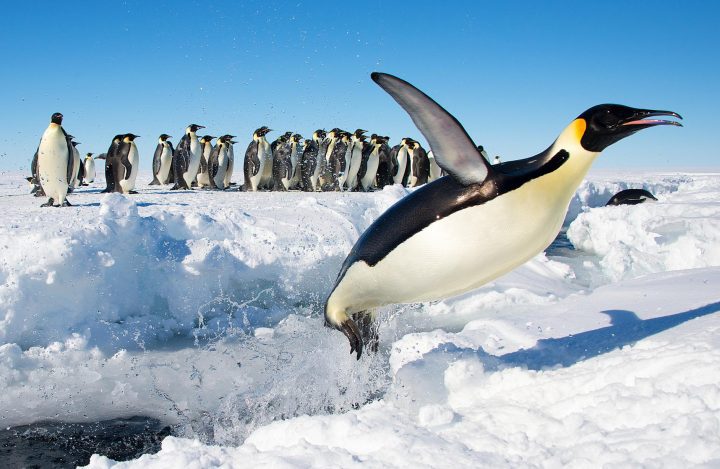
Buoyancy is an upward force exerted by air or liquid on a solid object that works against the object’s weight. A hawk glides through air and a duck floats on water due to buoyancy. Some living systems (such as fish eggs) can remain sedentary and therefore maintain the same buoyancy at all times. But most must adjust their buoyancy because they can’t survive long unless they change position. These living systems require strategies to not only be buoyant, but also adjust buoyancy level. They often modify buoyancy by adding or decreasing lift, or by changing their weight. For example, birds like condors that soar for a long time shift the directional orientation of their wingtip feathers to manage buoyancy. Fish alter the amount of air in their swim bladders to increase or decrease their weight, thus altering their buoyancy.