Modify Size/Shape/Mass/Volume
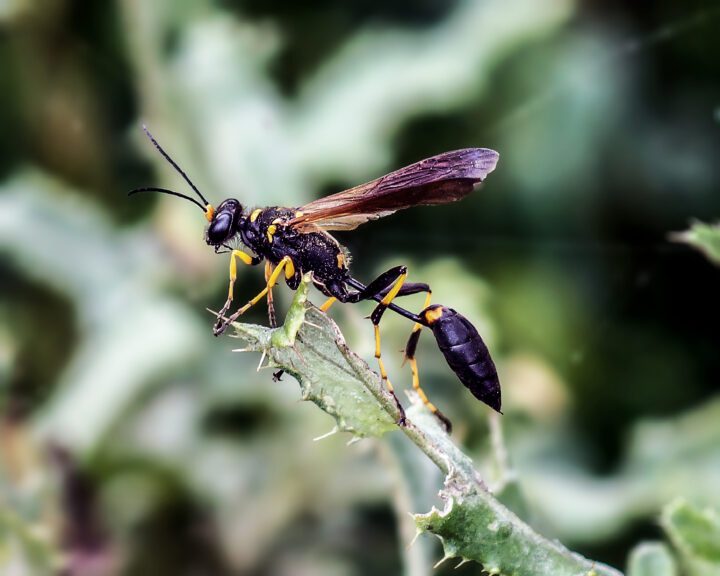
Many living systems alter their physical properties, such as size, shape, mass, or volume. These modifications occur in response to the living system’s needs and/or changing environmental conditions. For example, they may do this to move more efficiently, escape predators, recover from damage, or for many other reasons. These modifications require appropriate response rates and levels. Modifying any of these properties requires materials to enable such changes, cues to make the changes, and mechanisms to control them. An example is the porcupine fish, which protects itself from predators by taking sips of water or air to inflate its body and to erect spines embedded in its skin.
Protect From Loss of Liquids
Water is essential to life. Liquids, mostly water, make up 70 to 90% of all living systems, and the loss of even a small percentage can mean the difference between life and death. Living systems must maintain a proper liquid balance, which is especially difficult in dry conditions. To do so, they must control the movement of liquids across their boundaries. Living systems do this using structures or waterproof materials to prevent or slow liquid movement. For example, when humans receive a cut, they must limit blood loss. Scattered throughout the bloodstream are lens-shaped structures that serve to plug the wound.