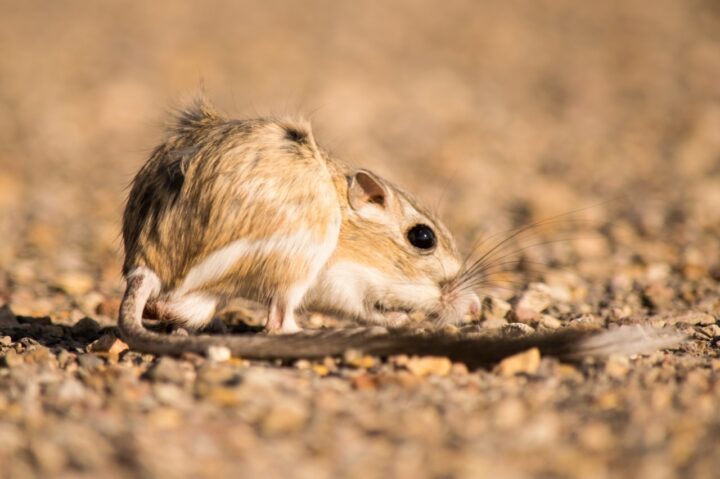
The flower petal nests of Osmia avosetta bees are durable and humid because of their multi-layer design, with a hard layer sandwiched between organic layers.
Physically Assemble Structure
Living systems use physical materials to create structures to serve as protection, insulation, and other purposes. These structures can be internal (within or attached to the system itself), such as cell membranes, shells, and fur. They can also be external (detached), such as nests, burrows, cocoons, or webs. Because physical materials are limited and the energy required to gather and create new structures is costly, living systems must use both conservatively. Therefore, they optimize the structures’ size, weight, and density. For example, weaver birds use two types of vegetation to create their nests: strong, a few stiff fibers and numerous thin fibers. Combined, they make a strong, yet flexible, nest. An example of an internal structure is a bird’s bone. The bone is comprised of a mineral matrix assembled to create strong cross-supports and a tubular outer surface filled with air to minimize weight.
Protect From Loss of Liquids
Water is essential to life. Liquids, mostly water, make up 70 to 90% of all living systems, and the loss of even a small percentage can mean the difference between life and death. Living systems must maintain a proper liquid balance, which is especially difficult in dry conditions. To do so, they must control the movement of liquids across their boundaries. Living systems do this using structures or waterproof materials to prevent or slow liquid movement. For example, when humans receive a cut, they must limit blood loss. Scattered throughout the bloodstream are lens-shaped structures that serve to plug the wound.

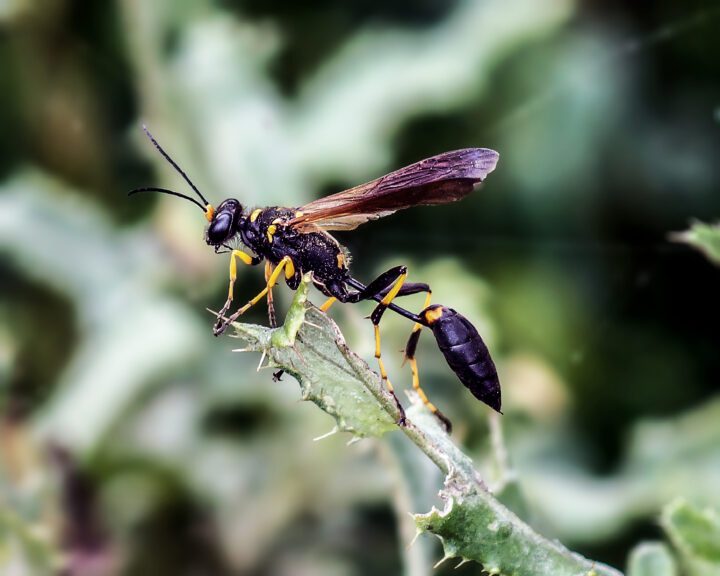
Insects
Class Insecta (“an insect”): Flies, ants, beetles, cockroaches, fleas, dragonflies
Insects are the most abundant arthropods—they make up 90% of the animals in the phylum. They’re found everywhere on earth except the deep ocean, and scientists estimate there are millions of insects not yet described. Most live on land, but many live in freshwater or saltwater marshes for part of their life cycles. Insects have three distinct body sections: a head, which has specialized mouthparts, a thorax, which has jointed legs, and an abdomen. They have well-developed nervous and sensory systems, and are the only invertebrate that can fly, thanks to their lightweight exoskeletons and small size.