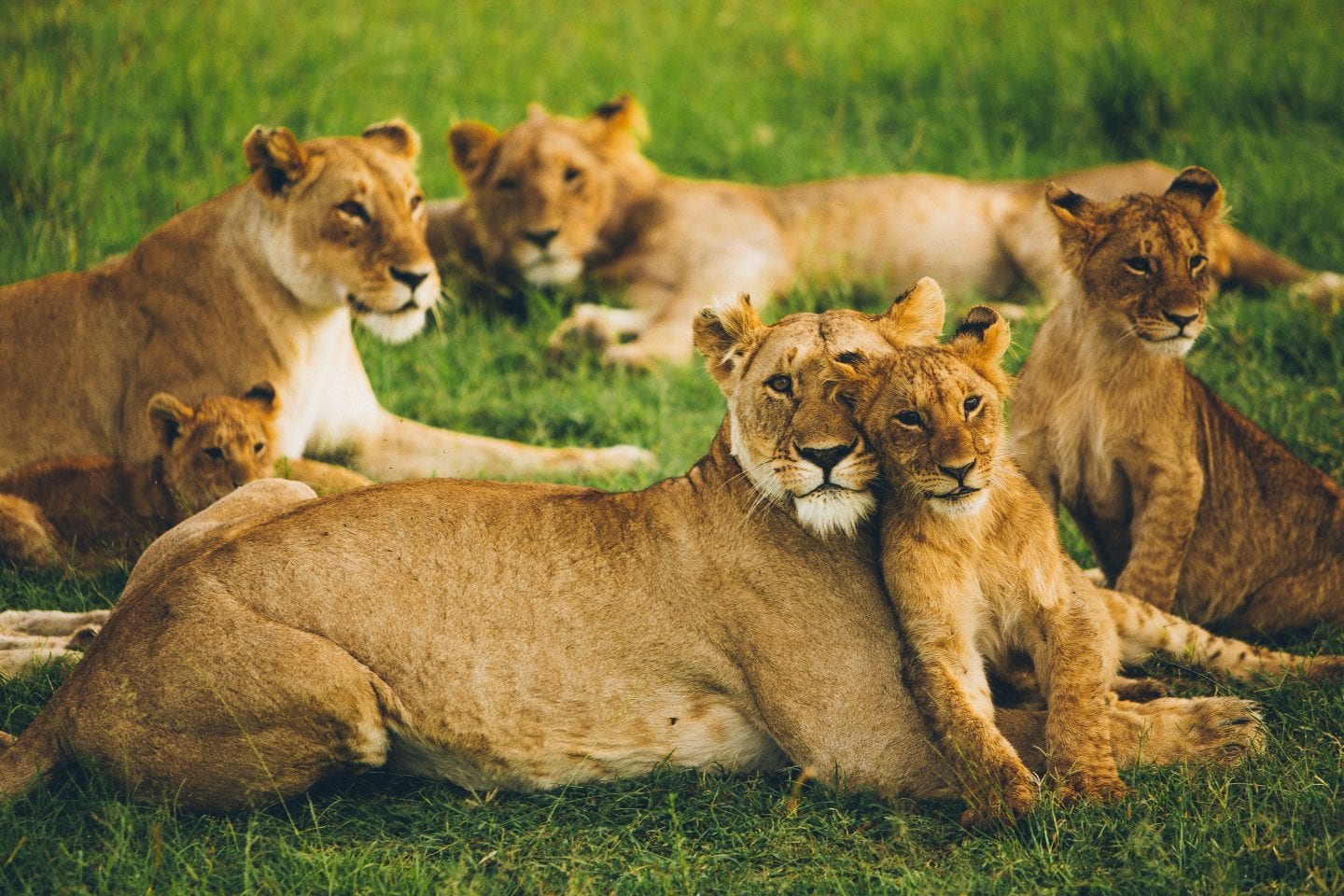
Maintain Homeostasis
When a living system is in homeostasis, it means that internal conditions are stable and relatively constant. For example, a human’s internal temperature is approximately 37 degrees Celsius (98.6 degrees Fahrenheit) unless there’s an illness. The human body maintains this temperature despite external ambient temperature. However, as with all physiological processes, maintaining homeostasis requires communication and coordination. So living systems have ways to detect changes from the norm, mechanisms to cause an adjustment, and negative feedback connections between the two. A desert lizard called the Gila monster offers a good example of maintaining homeostasis. The lizard goes from eating large meals to fasting for extended time periods. To maintain its blood sugar levels at a steady level, when food is scarce, its endocrine system releases a hormone that raises its blood sugar levels.
Distribute Liquids
Liquids include water, as well as body fluids such as blood, gastric juices, nutrient-laden liquids, and more. To survive, many living systems must move such liquids within themselves or between locations. Because of their properties, liquids tend to disperse unless they are confined in some way. To address this, living systems have strategies to confine fluids for transport, and to overcome barriers such as gravity, friction, and other forces. Some of these same barriers also provide opportunities. Trees and giraffes face the same challenge: how to move fluids (water and blood, respectively) upward against gravity. But their strategies are quite different. The tree moves water using capillary action and evaporation, possibly due to water’s properties of polarity and adhesion. The giraffe’s tight skin provides pressure to assist in blood circulation. and keep blood from pooling in the legs.