Water purifier from Princeton University is made of a hydrogel that expands and contracts to extract contaminants from water.
Benefits
- Reduced costs
- Non-toxic
- Efficient
Applications
- Water filtration
- Water treatment
UN Sustainable Development Goals Addressed
-
Goal 3: Good Health & Wellbeing
-
Goal 9: Industry Innovation & Infrastructure
The Challenge
Water is essential for human survival, and access to clean drinking water is critical for good health. Contaminated drinking water can cause numerous health concerns, namely exposure to bacteria and viruses. However, wastewater treatment systems can be expensive to build and require specialized materials, making them inaccessible in many places. Moreover, the impacts of climate change will soon make it harder than ever to acquire clean water in vulnerable locations, endangering human health and straining vital energy resources. Therefore, any technologies that extract potable water from tainted sources must be environmentally friendly.
Innovation Details
The solar absorber gel (SAG) consists of three layers, resembling a large sponge that soaks up water while removing pollutants like pathogens, lead, and oil. The innermost layer is composed of a sponge-like elastic gel, called a hydrogel. The hydrogel holds water between its long entangled polymers, and when heated, the structure contracts, squeezing out excess water. Surrounding this hydrogel is a layer of melanin-based molecules that absorb sunlight to provide energy to the purifier. This layer is also capable of removing heavy metals and organic dyes through chemical bonding, doing so as excess water is squeezed out of the inner hydrogel. Lastly, the outer layer is a filter layer that blocks impurities and pathogens. Altogether, the purifier exhibits efficient production of high-quality water in remote locations.
Biomimicry Story
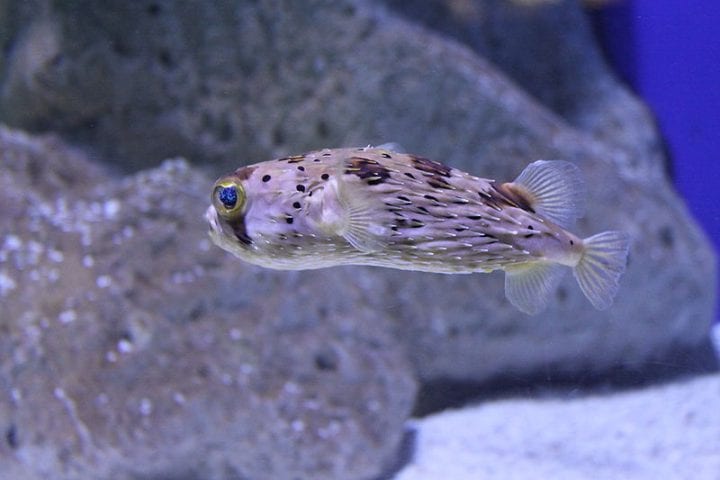
The team was inspired to create this condition-based water-holding gel by the condition-based water retention of pufferfish. When in danger, pufferfish take in water to enlarge their bodies and raise their spines, making them appear larger and more threatening to predators. Once the threat is gone, the fish release the water and return to a smaller form. Similarly, the solar absorber gel takes in water when relatively cool, and then releases it when slightly warmed by the sun.





