Solar cell from University of Illinois Chicago uses sunlight to recycle carbon dioxide into a renewable fuel source.
Benefits
- Scalable
- Efficient
- Reduced costs
Applications
- Commercial and industrial energy generation
UN Sustainable Development Goals Addressed
-
Goal 7: Affordable & Clean Energy
-
Goal 11: Sustainable Cities & Communities
-
Goal 13: Climate Action
The Challenge
Human-caused greenhouse gas emissions are at the highest levels ever recorded. These gases absorb solar energy and keep heat close to the Earth, also called the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gas, carbon dioxide, is emitted from burning fossil fuels.
Innovation Details
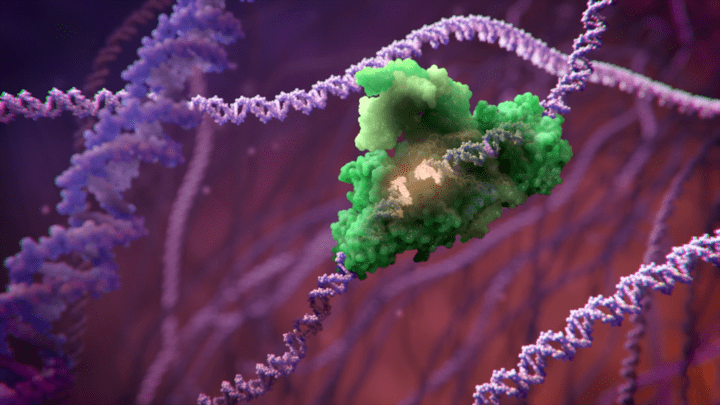
The solar cells use an integrated system that combines carbon capture with artificial . The system converts carbon dioxide and water collected from the atmosphere into a usable hydrocarbon gas using sunlight. The inner unit absorbs sunlight, adding heat that enables s inside the unit to convert carbon dioxide and water into a mixture of hydrocarbons. The resulting synthetic gas, called syngas, can be utilized as fuel.
Biomimicry Story
Photosynthesis is essential for life on Earth. It is the process by which plants produce energy and oxygen using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide.