Algorithm from Stanford is parameterized by field data enabling it to quickly fix network disruptions.
Benefits
- Efficient
- Systematic
- Adaptive
Applications
- Search engine optimization
- Utilities
UN Sustainable Development Goals Addressed
-
Goal 11: Sustainable Cities & Communities
The Challenge
Sampling methods used in many probability-based algorithms do not track previously sampled components. This methodology leads to inefficiency because the program cannot remember what it has already done and could end up repeating the process.
Innovation Details
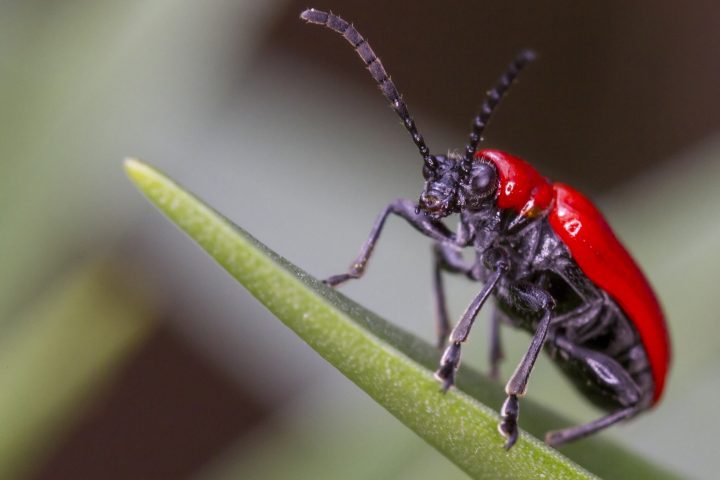
The search algorithm is developed using field data based on ant behavior. It is a distributed algorithm in which there is no centralized controller but rather individual agents monitoring the system. The algorithm efficiently circumvents network disruptions using fewer computational resources, which increases efficiency.

Biomimicry Story
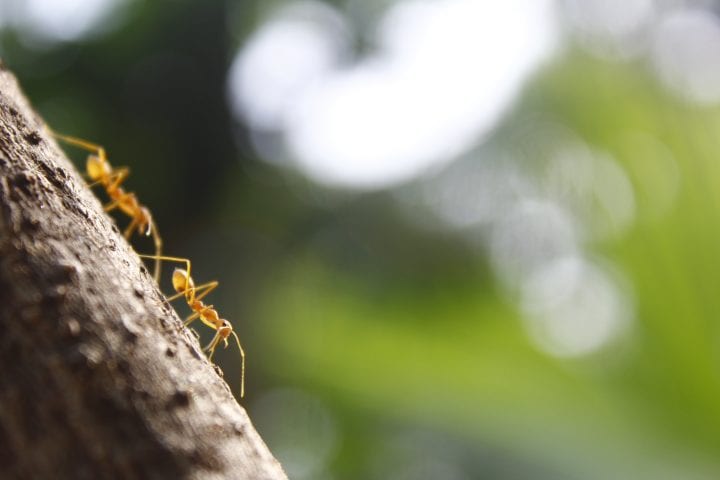
Arboreal ants, such as the arboreal turtle ant, maintain trail networks that connect their nests to their food sources. If a trail is disrupted, they retrace their steps and follow the next most efficient path at the previous junction. The ants leave pheromones as they walk the paths, but the chemicals slowly evaporate, enabling the other ants to find the most recently used path.






